Effective Diversification
ETFs offer broad diversification by replicating entire indices, thus reducing the risk associated with a single company or sector.
Discover why ETFs have become essential for savvy investors
ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds) are index funds that can be traded on the stock exchange and passively track a specific index. Their growing popularity is explained by numerous advantages over investing in individual stocks.
ETFs offer broad diversification by replicating entire indices, thus reducing the risk associated with a single company or sector.
Thanks to their passive management, ETFs have significantly lower management fees than actively managed funds, which improves long-term returns.
ETFs offer great transparency on their components and performance, allowing investors to make informed decisions.
ETFs can be bought or sold at any time during stock market hours, offering great flexibility to investors.
ETFs benefit from a self-cleaning effect: poorly performing companies are automatically excluded from the index and replaced by more promising companies.
There are two main types of ETFs: accumulating and distributing. Each has its advantages depending on your investment goals.
Accumulating ETFs automatically reinvest dividends, which maximizes the compound interest effect and can be tax-advantageous.
Distributing ETFs regularly pay out dividends, which may suit investors looking for regular income.
ETF taxation in the UK varies depending on the type of investment account used. It's crucial to understand these differences to optimize your investments.
In the UK, ISAs (Individual Savings Accounts) offer significant tax advantages for ETF investments, particularly in the long term.
Gains from ETFs in a standard brokerage account are subject to capital gains tax, which can be up to 20% for higher rate taxpayers.
ISAs benefit from a favorable tax regime with no tax on capital gains or dividends, regardless of the amount invested.
ETFs like the MSCI World or the S&P 500 have demonstrated remarkable long-term performance, often outperforming actively managed funds.
The MSCI World, an index representing developed world markets, has generated an average annual return of about 10% since its inception.
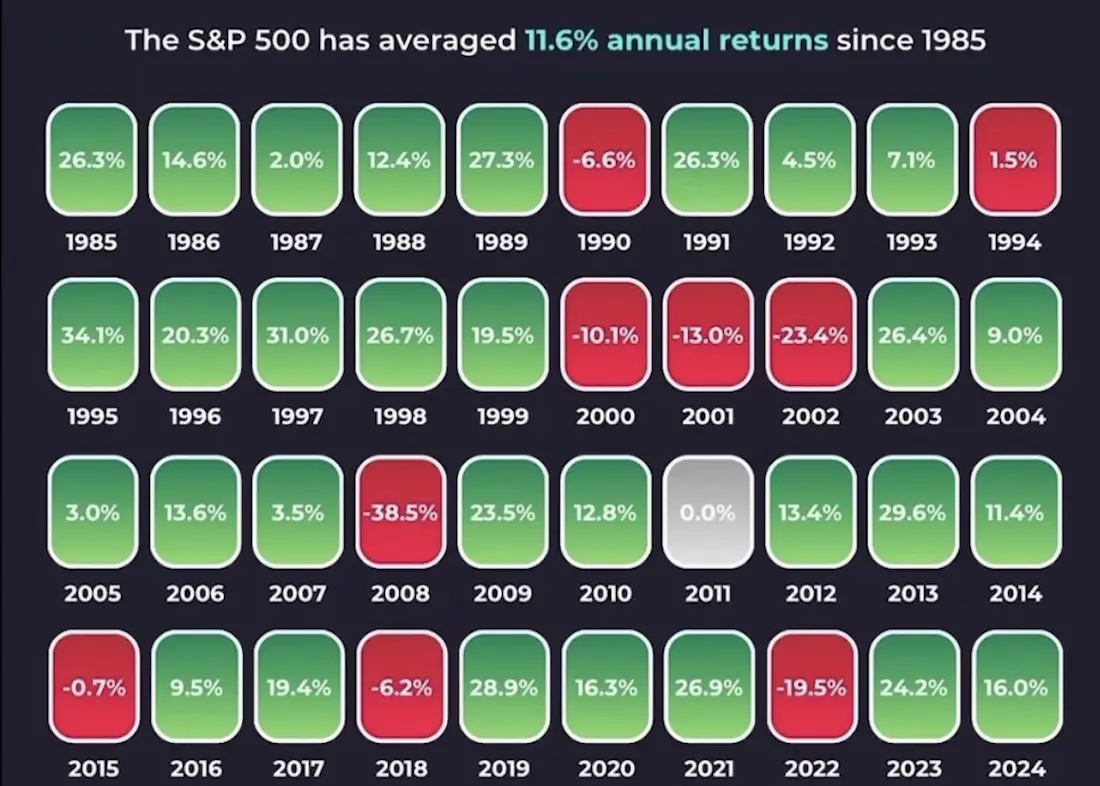
The S&P 500, which tracks the 500 largest listed companies in the United States, has achieved an impressive average annual return of about 12% since its creation.
In the UK, there are several options for investing in ETFs, each with its own tax advantages and particularities:
ISAs are ideal for UK investors looking to invest in ETFs while benefiting from significant tax advantages.
After opening an ISA, capital gains and dividends from ETFs are not subject to tax, regardless of the amount invested. This favorable tax regime applies to an annual contribution limit set by the government.
A GIA offers more flexibility in terms of ETF choice, including non-European ETFs, but with less favorable taxation than ISAs.
Capital gains realized on a GIA are subject to capital gains tax, which can be up to 20% for higher rate taxpayers. This tax applies from the first pound of profit above the annual exemption.
When it comes to investing in ETFs, the choice of platform is crucial. It's important to consider fees, ease of use, and the range of products available.
At leFullStack, we personally use Boursobank for our ISA. Although there are many other advantageous banks, we chose Boursobank because of its management and order fees, which are among the most competitive in the market.
For any first opening of a bank account with a first deposit, followed by an EasyMove bank transfer:
Securities involve a risk of capital loss; any investment should be considered over the medium or long term.
ETFs offer an efficient, diversified, and low-cost investment solution, suitable for both beginners and experienced investors. Their simplicity, transparency, and historical performance make them a wise choice for building wealth over the long term.
Ilane Lopez
Founder / CTO